Corporate hierarchy data: the central spoke in an organization’s wheel to leverage account intelligence and channel insights into crucial market decisions.
Despite its mainstream presence, definitions of corporate hierarchy vary. From a business standpoint, hierarchy outlines how an organizational structure is spread across geographical boundaries, with various interconnected entities. A firm’s overall business strategy, the relative size of worldwide operations, and marketplace characteristics determine its hierarchy.
The term is used synonymously with organizational structure and corporate structure. But the key difference between hierarchy and structure is that hierarchy includes multiple companies stemming from a headquarters, whereas structure describes the chain of command by employee roles.
Corporate Hierarchy vs. Organizational Structure
Hierarchy helps discover parent-child relationships between subsidiaries, divisions, brands, and branches. It identifies different organization names and tracks changes in corresponding business markets.
Organizations continually gather and break down hierarchy data for building robust account strategies. Understanding the link between corporate hierarchy and account intelligence helps streamline Go-To-Market (GTM) activities.
Typically, as business expands, the span of control widens. So when an organization becomes relatively stable, flexibility may decrease, adversely impacting creativity and growth. Adapting accounts to the hierarchy of corporate titles with changing market and competitor situations secures recovery from growth fatigue.
Getting corporate hierarchy right is essential for facilitating smooth working relationships among multiple organizational entities. It also improves the working efficiency of individual units and the parent firm, and sets up the business for market success.
So, how does a corporate hierarchy database fit into targeted sales and marketing campaigns?
Data Maturity + Corporate Hierarchy: Developing Targeted Account Strategies
Firms with increased data maturity – i.e., how well they can leverage data in decision-making for crucial business outcomes – experience growth in revenue, improved efficiency, better customer lifetime values (LTV), and higher net promoter scores (NPS). Product teams using data analytics, tools, and processes see 2.5 times better business results than data immature teams.
Indeed, data maturity can be a game-changer for organizations, enabling them to capture a larger market share in highly competitive markets.
How is this particularly beneficial for GTM teams?
Consider what happens with poor data maturity. Sales and marketing teams develop a narrow outlook by looking at internal information and losing perspective of the overall organizational vision. Data silos lead to teams working disjointly and making local, disconnected decisions.
Data maturity promotes the seamless and frequent transfer of information among subsidiaries, departments, and functions. So data-mature organizations tackle information silos using a centralized data store and defined data standards. This provides a clear overview of company-wide plus global activities and continually unlocks new insights.
However, initiating complex corporate hierarchies to leverage data is not necessary.
For instance, HG Insights’ account intelligence provides granular information about an organization’s global account activities, IT spend, and technology installs. It lets businesses determine the location of their ideal customer profile (ICP) and what are the account activity hotspots to optimize resource allocation and hyperfocus on target accounts.
Introducing Corporate Hierarchy Data in Sales & Marketing Campaigns
Here are 7 key considerations for businesses to leverage a corporate hierarchy database in targeted sales and marketing campaigns.
1. Review Sales Organization Structure
It starts with determining the sales organization structure in terms of segmentation, regions, and roles.
Businesses must set up parameters for defining enterprise-level and mid-market corporations and lay down responsibilities for account teams. There may be additional segmentations and verticals to review for developing a dynamic but best-suited sales structure.
Prominent models include:
- Centralized account team handling all global sales activities.
- Account teams assigned to sales responsibilities based on regions (territory-based).
- Sales teams own subsidiary-based accounts that may or may not be similar to regional accounts.
- Customized account ownership based on business needs.
2. Undertake Territory Planning
Territory planning is a crucial activity to facilitate sales and marketing processes. Companies must determine how often they need to undertake territory planning and if all sales reps are equitably assigned areas.
Also consider data’s role in building territories and establishing sales quotas by leveraging historical insights and streamlining next year’s territory planning.
HG Insights IT Spend Intelligence feature uses past data, such as market-level trends and company cohort analysis, to develop an estimated IT spend, updated every six months for the latest insights.
Technology Installs shares details of an organization’s technology products, capturing new installs and updating existing data. Teams can track granular information through corporate hierarchy, from country (broad) to metro area (narrow).
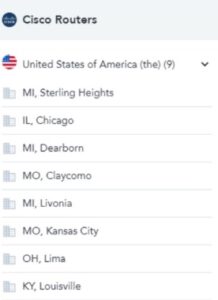
These features support the territory planning process, allowing sales teams to focus on areas where target accounts are positively progressing.
3. Identify & Manage Accounts
Continued business growth results from having a robust sales pipeline by attracting new opportunities and keeping existing ones satisfied.
To acquire new accounts, sales teams first need to identify profitable and viable opportunities across an organization’s corporate titles hierarchy and repeat the process for multiple organizations.
Coupled with data governance, sales and marketing teams also need to ensure that clean CRM practices are followed, mitigating risks of bad data while upholding compliance. At the individual level, sales reps should be able to create data-compliant accounts by following the proper criteria.
Companies must evaluate vendors (both new and current) that secure organizational and individual-level accounts without compromising on quality intelligence.
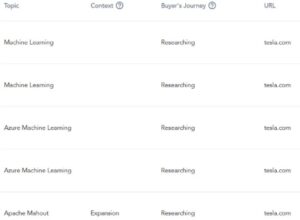
Functional Area Intelligence uncovers personas within the corporate hierarchy database by evaluating technology install insights and attributes. Businesses get intelligence on department, location, and competition-based operations. It’s backed by Contextual IntentTM, highlighting a company’s real-time research into IT spend and exposing buyer intent.
Sales and marketing teams can use these actionable insights to develop a refined approach for target markets.
4. Structure & Score Accounts
Corporate hierarchy ensures that account assignment combines internal capacity and market opportunity. Organizations have a clear demarcation for splitting accounts between the parent company and subsidiaries across segments, regions, and roles.
This distribution further enables developing best-fit approaches for scoring and propensity modeling. IT Spend intelligence breaks down corporate hierarchy data for a dynamic understanding of organizational tech stacks, giving teams the means to score accounts and optimize resource allocation.
Functional Area Intelligence and Contextual Intent further improve GTM outcomes by using corporate hierarchy to showcase buyer intent, encourage sales reps to engage with prospects and deliver relevant value.
5. Align Sales & Marketing Teams
Sales and marketing alignment has long been an area of contention for GTM success. Misalignment between departments doesn’t sit well with buyers, as more than 97% of sales and marketing professionals concur that poor collaboration negatively impacts business outcomes.
Data mature firms have processes to support cross-functional collaboration, particularly between the above two functions. While it’s easier to achieve peer-to-peer collaboration, ensuring reps work seamlessly alongside sales and marketing leadership gives organizations an extra edge.
Primary functions also need to partner with ancillary departments for holistic support of GTM activities and reach target accounts via more refined, targeted approaches.
6. Track Sales Attrition
Marketplaces are increasingly competitive today, so much so that even the most robust data sets may not paint a comprehensive and diverse picture to identify key organizational stakeholders. In this scenario, corporate hierarchy data becomes critical for enterprise sales teams to gather account intelligence and discover where key buying centers lie.
The downside of competitive markets is losing sales and marketing reps to attrition, negatively impacting revenue. Less data mature firms risk slowing down sales velocity with insufficient or irrelevant data, shallow insights into prospects, and longer sales cycles – all of which demotivate teams from pursuing complex and rewarding accounts.
With data on IT Spend, Technology Installs, Functional Area Intelligence, and Contextual Intent, sales and marketing teams access clues about where buying will happen and strike when the opportunity is hot. It doesn’t take a lot to understand that higher win rates = happy sellers.
7. Set Success Metrics
Success metrics have a multifold purpose – identify areas of improvement, evaluate the current business position, and track changes in performance. They hold the key to understanding data’s overall impact and maturity level.
A few success metrics relevant to sales and marketing campaigns include:
- Sales quota attainment (further classified by account size, location, product and more)
- Win rate
- Average deal size
- Expansion rates of existing accounts
- Number of touchpoints to book a meeting
- Number of touchpoints to transform meetings into opportunities
- Sales attrition rate
Some metrics are quickly arrived at, while others, such as the expansion rate of an existing account, may need additional insights but provide richer intelligence.
The Bottom Line
Actionable intelligence from corporate hierarchy databases helps construct a path for successful business outcomes. Our platform at HG Insights gives you granular account information based on functional areas, buying intent, technological spends, and competitive market opportunities.
This blog is only a starting point. Download our free in-depth guide for corporate hierarchy activation and unearth valuable insights for market analysis, strategic planning and frontline execution.